
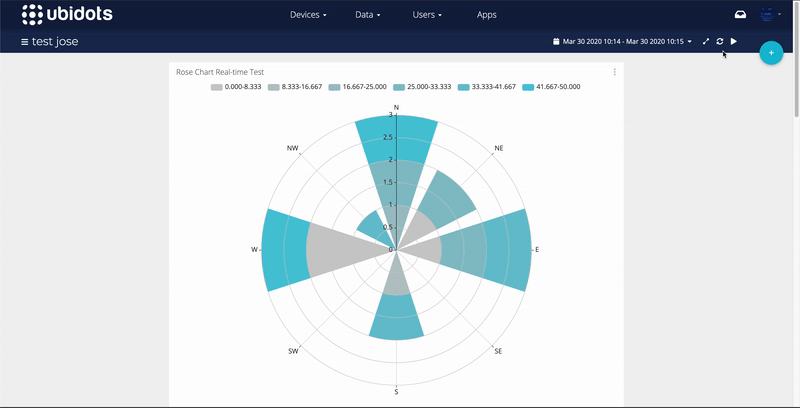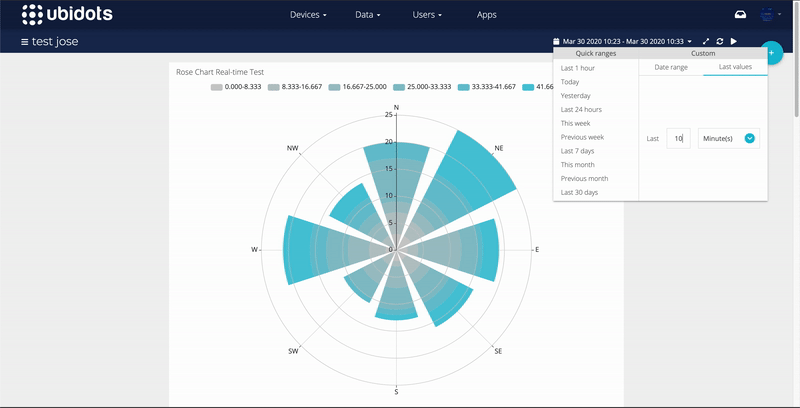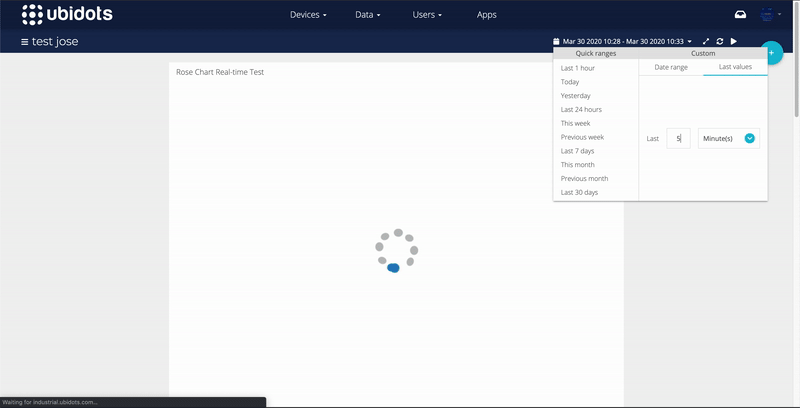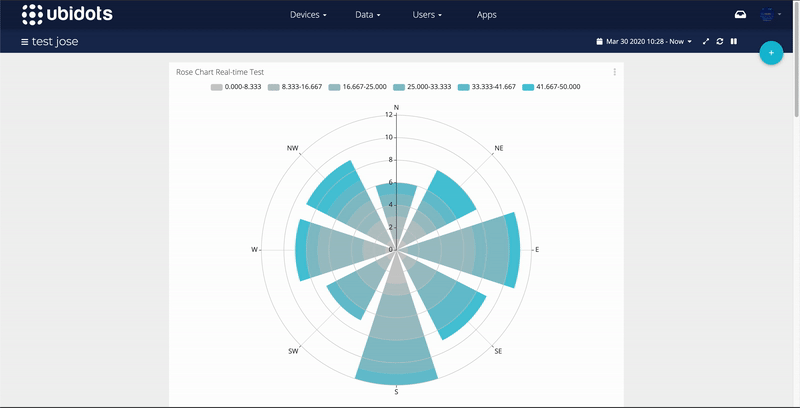
As anybody who has wrestled with converting these two coordinate systems can tell you, it would have been lovely if the geographers and geometers had agreed on a single coordinate system. Furthermore, the origin of a unit circle is on the right side (east), compared with a compass, where the origin is at the top (north). Values on a unit circle increase counterclockwise whereas those on a compass increase clockwise.

The ones I have tried are less desirable because they follow unit circle coordinates rather than compass coordinates, which differ in two important ways. There are other ways to plot rose diagrams, like compassRose in the sp package. Rose.diag(x.circ, bins=18, col="gray", border=NA) X.circ <- circular(x, type="directions", units="degrees", template="geographics", rotation="clock") Second, the rose diagram is constructed, which may include setting the number of bins, setting the color, turning off the border, etc. First, the data must be converted to a circular object, which means specifying that the data are directions, in degrees, are geographically referenced, and that the values increase clockwise. The polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional system in which each point on a plane. In this article we’ll discuss and show the Matlab built-in commands compass, polar and rose. If you later want to use the default versions of sd and var, you can detach the circular package by calling detach("package:circular").īuilding the rose diagram is a two-step process. Polar Plots (with a little help from Matlab) Matlab provides functions that produce polar plots in appropriate coordinates using magnitudes and angles. Loading the circular package warns you that the default functions sd and var are masked, being replace with those from the package. The circular package makes constructing rose diagrams simple. Rose diagrams solve both of these problems by displaying the frequency distribution radially. More important, it fails to convey that the scale wraps around: 10° and 350° are numerically very different than 10° and 30°, but their angular differences are identical. A standard histogram does a poor job of this, partly because it doesn’t show directions as on compass.
ROSE CHART VS ROSE DIAGRAM HOW TO
Reserve your seat and order your tickets today! Visit the events page to get started.įor more information on the ticket policy and the preferred ticket provider please view the Rose Bowl Stadium tickets page.įor all upcoming events at the Rose Bowl Stadium please view the Rose Bowl Stadium events page.When we collect directional data, such as paleocurrent or wind directions, we need a way to show their frequency distribution. 80)) > Do you have any idea how to plot the other 2 variables freq2 and freq3 by > R > Nightingales Rose chart actually represent 3. Follow Gate D and you shall be in the stadium within five minutes! Don’t bother to try to squeeze in with the crowd at other gates. So, if it's dynamic charts, you'll need a lot of these words like increase, decrease, doubled, tripled, decreased and so forth, fell, rose, all this kind of language whereas in these static charts while you don't need all that vocabulary, what you do need is a lot of this language of comparison. Tip! Gate D is usually the least crowded entrance. There are almost no bad seats in the Rose Bowl Stadium as commented by fans who have attended events there. These levels are further split into categories like Club Seats, Loge Boxes, E Level Suites, and F Level Suites.

Supported importing Swagger, OpenAPI, YAML and JSON. Visual Paradigm 16.3 introduces a number of new features, which includes: Support of OpenAPI specification v3 in API generation.
Seats are split into three main levels which are level D, E, and F. Visual Paradigm International Limited announced today the release of Visual Paradigm 16.3. The current seat capacity is approximately at 92,542 seats. The stadium was remodeled in 2014 and this renovation removed the lower-lettered row seats on each side behind the players’ benches. The number of attendees was far below the number of seats available. As some of the seats closest to the field were never used during UCLA regular season games, official capacity was lowered. Make sure you check the individual seating map when selecting your tickets.įrom 1972 to 1997, the maximum seating capacity was at 104,091. NOTE: Seating layouts may change depending on the event.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
